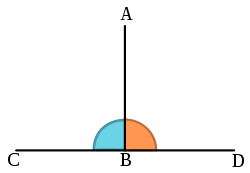Range
Range- The positive difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set.
To find range you must: you take the highest number in the data set minus by the lowest number in the set then it will equal the range.
Friday, June 15, 2012
Quadrant
(+,+) quadrant I (-,+) quadrant II (-,-) quadrant III (+,-) quadrant IV
Thursday, June 14, 2012
Range
Eg.
range of 4,8,5,6,9,1,3,5,8,6 is
1,3,4,5,5,6,6,8,8,9
9-1 = 8
Mean
A measure of central tendency
the sum of a set of values divided by the number of
values in the set
mean of 6,4,8 is
add up all the numbers and divide the results by how many numbers there are
6+4+8=18
18 divide it by 3 = 6
therefor the mean is 6
Mode
set of data
mode and most both have 4 letters
Eg.
mode of 3,5,7,7,9 is 7
mode of 2,2,4,6,6,8,11 is 2 and 6
Median
The middle number in a set
of data after the data have been arranged in order
Eg.
median of 2,5,6,8,9 is 6
median of 1,3,6,8,9,10 is 7
of data after the data have been arranged in order
Eg.
median of 2,5,6,8,9 is 6
median of 1,3,6,8,9,10 is 7
Definition & How to = Outliers
Outliers: Numbers that have small values and numbers that have large values
How to:
ex . 1 , 99 , 99 , 9001 = 1 & 9001
ex . 16 , 4 , 6 , 9 = 16
How to:
ex . 1 , 99 , 99 , 9001 = 1 & 9001
ex . 16 , 4 , 6 , 9 = 16
Definition & How to = Mode
Mode: Most occurring number on a data set
How to find it:
ex...
6 , 5 , 1 , 5 , 7 = 5
Multiples can occur, even no mode at all.
ex...
7 , 1 , 9 , 2 , 8 ≠ No Mode
6 , 9 , 0 , 6 , 9 = 69 or 6 & 9
How to find it:
ex...
6 , 5 , 1 , 5 , 7 = 5
Multiples can occur, even no mode at all.
ex...
7 , 1 , 9 , 2 , 8 ≠ No Mode
6 , 9 , 0 , 6 , 9 = 69 or 6 & 9
Height & Base Definitions
Height or 'h': Vertical distance from the top of an object or figure to its base.
Base or 'b': Surface of an object or the line.
Base or 'b': Surface of an object or the line.
Integer / Chips
○ = Positive
● = Negative
|――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――|
ex #1...
If Timmy has has 5 cows and somebody stole 3, how many does Timmy have left?
A . ○○○○○ - ●●● = 2
How?
○○○|○○
●●● |
Left = 2 / ○○
●+○ = 0x3 (x3 because there's 3 negatives)
|―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――|
ex #2 in numbers
*** Same Question ***
In numbers, how?
5 = ○○○○○ (-3) = ●●●
5-(-3) = 2 or ○○
|――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――|
● = Negative
|――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――|
ex #1...
If Timmy has has 5 cows and somebody stole 3, how many does Timmy have left?
A . ○○○○○ - ●●● = 2
How?
○○○|○○
●●● |
Left = 2 / ○○
●+○ = 0x3 (x3 because there's 3 negatives)
|―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――|
ex #2 in numbers
*** Same Question ***
In numbers, how?
5 = ○○○○○ (-3) = ●●●
5-(-3) = 2 or ○○
|――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――|
!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!MATH!
Mean,Median,Mode,Range,Outlier
Mean-Add up all values divide by how many values there are
Median- The middle number in a set of ordered values, might be the mean of 2 middle values
Mode- The value that shows up the most
Range- Positive difference between largest and smallest values
Outlier-Values that are too big or too small compared to the other values
Median- The middle number in a set of ordered values, might be the mean of 2 middle values
Mode- The value that shows up the most
Range- Positive difference between largest and smallest values
Outlier-Values that are too big or too small compared to the other values
Wednesday, June 13, 2012
Mode & Range
Mode- The value that shows up the most
Range- Positive difference between largest and smallest values
Range- Positive difference between largest and smallest values
Mean & Median
Mean- Add up all values by how many values there are
Median- The middle number in a set of ordered values might be the mean of 2 values
Median- The middle number in a set of ordered values might be the mean of 2 values
How to do a circumference question
Hi i'm back again and today I'm going to show you how to to do a circumference question
lets say the question is d=2 m
1 c=d x 3.14 ( 3.14 is pi)
2 c= 2 x 3.14
c=6.28
lets say the question is d=2 m
1 c=d x 3.14 ( 3.14 is pi)
2 c= 2 x 3.14
c=6.28
How to do two step algebraic equations
here's how you do it lets say the question is 4t-2=10
opposite order of operations
4t-2=10
4t-2+2 = 10 + 2
4t =12
4t/4 = 12/4
t=3
opposite order of operations
4t-2=10
4t-2+2 = 10 + 2
4t =12
4t/4 = 12/4
t=3
how to add opposite integers
this how to add opposite integers lets say the integers are 5 and (-10so take what you know about zero pares 5 is smaller value wise than (-10) so take negative 5 away for now then add 5 + (-5) = 0 so whats left the (-5) that we left alone while we made a zero pare so that's how to add opposite integers see you latter every body
What is a zero pare
A zero pare is when two two opposite numbers of the same value are added together to make zero
here is an eg. for you yo look at eg. 8 + (-8)=0 there you that is a zero pare
here is an eg. for you yo look at eg. 8 + (-8)=0 there you that is a zero pare
How to subtract Mixed numbers
This is howto subtract mixed nubers
same thing as befor deal with the fractions first
then the whole numbers 7/10 - 3 1/1 0= 2 6/10
there you have how to subtract mixed numbers
same thing as befor deal with the fractions first
then the whole numbers 7/10 - 3 1/1 0= 2 6/10
there you have how to subtract mixed numbers
How to add mixed numbers
If you have problems with add mixed numbers watch this
step 1 get rid of the fractions first
step 2 deal with the whole numbers
Now watch this eg. 1 2/3 + 4 2/6
2/3 + 2/6 = 1
1 + 1 + 4 = 6
there you have it
step 1 get rid of the fractions first
step 2 deal with the whole numbers
Now watch this eg. 1 2/3 + 4 2/6
2/3 + 2/6 = 1
1 + 1 + 4 = 6
there you have it
How to solve one step aljerbra problems
This is how to solve one step aljerbra problems
step 1 lets say this is the problem a+6=10
step 2 oppisite order of opperations so if it says + you have to - it a + 6 -10 = 4
A= 4
step 1 lets say this is the problem a+6=10
step 2 oppisite order of opperations so if it says + you have to - it a + 6 -10 = 4
A= 4
Tuesday, June 12, 2012
Median.
The median is the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order from least to greatest.
for example- 5,6,7,8,9 the median is 7.
for example- 5,6,7,8,9 the median is 7.
probabililty.
probability-likelihood or chance of an event occuring.
we determine this - favourable outcomes divided by possible outcomes.
what is the probability of the spinner landing on green?
we determine this - favourable outcomes divided by possible outcomes.
what is the probability of the spinner landing on green?
Mode.
The mode is the most frequently occuring number in a set of data.
Example-3,6,5,4,3,7 the mode is 3.
Example-3,6,5,4,3,7 the mode is 3.
MEAN
MEAN- measure of the central tendency
-the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in the set.
-the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in the set.
Monday, June 11, 2012
Wednesday, June 6, 2012
BEDMAS review
B.E.D.M.A.S is the order of operations:
B- Brackets
E- Exponents
D- Division
M- Multiplication
A- Addition
S- Subtraction
It all goes in order from Brackets to Subtraction
B- Brackets
E- Exponents
D- Division
M- Multiplication
A- Addition
S- Subtraction
It all goes in order from Brackets to Subtraction
Area of triangle and parallelogram formulas
Area of a triangle:
A= basexheight divided by 2
Area of a parallelogram:
A= basexheight
Math Exam Review II
The first one is Perpendicular Bisector- A line that that bisects another line into 2 equal parts
The second one is Angle Bisector- A line that bisects an angle
The third one is Intersecting- 2 lines that meet or cross
The fourth one is Parallel Lines- Lines in the same plane that never meet
The fifth one is Perpendicular- A 90 degree angle
Math Exam Review
Math Exam Review:
There are three types of Transformations:
1. Translation- Where the shape slides across the coordinate grid.
2. Rotation- When shapes turn around on a fixed point on the coordinate grid.
3. Reflection- When shapes are mirrored across a coordinate grid.
Outlier
Outlier- a value that is much larger or smaller that the other data value
- the data set may have more than 1 outlier or zero outliers
Outlier(s) for 24, 32,35,37,38,51 are 24 & 51
- the data set may have more than 1 outlier or zero outliers
Outlier(s) for 24, 32,35,37,38,51 are 24 & 51
Mean
Mean- a measure of the central tendency
-the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in the set.
Mean of 45,76,32
Add up all the numbers and divide the result by how many numbers there are
45+76+32
153/3
Mean= 51
-the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in the set.
Mean of 45,76,32
Add up all the numbers and divide the result by how many numbers there are
45+76+32
153/3
Mean= 51
Median
Median- the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order.
Median of 7,13,15,17,24 is 15
Median of 68,73,82,91,110 is 82
Median of 7,13,15,17,24 is 15
Median of 68,73,82,91,110 is 82
Mode
Mode is the most frequently occurring number in a set of data.
eg.
1,2,2,3 the mode is 2
3,3,4,4,5 the mode is 3 and 4
1,2,3,4 there is no mode
1,1,2,2,3,3 no mode
3,3,4,4,5,5,6 the mode is 3, 4, and 5
eg.
1,2,2,3 the mode is 2
3,3,4,4,5 the mode is 3 and 4
1,2,3,4 there is no mode
1,1,2,2,3,3 no mode
3,3,4,4,5,5,6 the mode is 3, 4, and 5
Outlier
Outlier is a value that is much larger or smaller than the other data value. The data may have more than one outlier or zero outliers. In other words it is the number that doesn't fit in the set.
eg.
2,96,97,98,99
The outlier is 2.
eg.
2,96,97,98,99
The outlier is 2.
Range
Range is the positive difference between the largest and smallest values in a a data set.
eg.
6,4,2,5,3,1
1,2,3,4,5,6
6-1=5
eg.
6,4,2,5,3,1
1,2,3,4,5,6
6-1=5
Mean and Median
Mean is a measure of central tendency. It is the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in a set. In other words add up all the numbers and divide the result by how many numbers there are.
eg.
3,5,7
3+5+7=15
15/3=5
Therefor the mean is 5.
Median is also a measure of central tendency. It is the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order.
eg.
3,0,1,7,3,2,6
0,1,2,3,3,6,7
The median is 3.
This is how you get the median if you have 2 numbers in the middle:
-Add the 2 numbers and divide the sum by 2.
1,2,3,4,5,6
3+4=7
7/2=3.5
The median is 3.5
eg.
3,5,7
3+5+7=15
15/3=5
Therefor the mean is 5.
Median is also a measure of central tendency. It is the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order.
eg.
3,0,1,7,3,2,6
0,1,2,3,3,6,7
The median is 3.
This is how you get the median if you have 2 numbers in the middle:
-Add the 2 numbers and divide the sum by 2.
1,2,3,4,5,6
3+4=7
7/2=3.5
The median is 3.5
Measures of Central Tendency
The Measures of Tendency is a value that represents the centre of a data set that can be the mean, median, or mode.
Data Set is a group of numbers that you must arrange in order from least to greatest.
eg.
6,6,8,3,2,7,5,9,0,4,6,7,8,3,2
0,2,2,3,3,4,5,6,6,6,7,7,8,8,9
Data Set is a group of numbers that you must arrange in order from least to greatest.
eg.
6,6,8,3,2,7,5,9,0,4,6,7,8,3,2
0,2,2,3,3,4,5,6,6,6,7,7,8,8,9
Monday, June 4, 2012
Outlier
A value that is much smaller then the outer data value
The data set may have more then 1 outlier or zero outliers
Eg. Outliers for 1, 67, 68, 67, 64, 65, 100 are 1 and 100
Mean
The sum of a set of values divided by the number of values
Eg. The mean of 6, 4, 8 is 6
Add up all the numbers then divide by how many numbers are in the data set
Eg. The mean of 6, 4, 8 is 6
Add up all the numbers then divide by how many numbers are in the data set
Mode
The most frequently occurring number in a set of data
Eg. The mode of 3, 5, 5, 6, 7 is 5 because there are 2 5's
Eg. The mode of 3, 5, 5, 6, 7 is 5 because there are 2 5's
Median
Median
The middle number of a set of data after the numbers are arranged in order
Eg. 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
The middle number is 3
The middle number of a set of data after the numbers are arranged in order
Eg. 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
The middle number is 3
Range
Range
The positive difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set
Eg. Range of 1, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9
9 - 1 = 8
The positive difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set
Eg. Range of 1, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9
9 - 1 = 8
Sunday, June 3, 2012
Range
Positive difference between largest and smallest values in a data set.
ex: 1,3,4,5,5,6,6,8,8,9
9-1=8
ex: 1,3,4,5,5,6,6,8,8,9
9-1=8
Measures of Central Tendency
A value that represents center of a data set.
Can be Mean, Median or Mode.
Can be Mean, Median or Mode.
Friday, June 1, 2012
outliers
A value that "lies outside" (is much smaller or larger than) most of the other values in a set of data.
range
The difference between the lowest and highest values.
In {4, 6, 9, 3, 7} the lowest value is 3, and the highest is 9, so the range is 9-3 = 6.
In {4, 6, 9, 3, 7} the lowest value is 3, and the highest is 9, so the range is 9-3 = 6.
median
- The median is the middle value, so I'll have to rewrite the list in order:
- 13, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 16, 18, 21
- 13, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 16, 18, 21